Columbus and the Sargasso Sea

The Sargasso Sea is located in the east side of the triangle in the middle of the Atlantic. It houses a few small islands and masses of clumped floating seaweed. A warm water current within it swirls clockwise, affecting the weather of the area, keeping it calm and steamy. Having little wind, this area greatly affects unpowered ships.
Christopher Columbus wrote in his diary about this sea. In fact, it so fooled his crew that it almost led them to mutiny.
There exists the possibility exists of never leaving this legendary sea, he wrote. Another fascinating feature he noted is its ability to draw things in from all over the Atlantic. Some even claim it to be the "catch-basin" of the Atlantic.
Columbus' crew was greatly disappointed when seaweed and land birds were sighted, but after a few days no land was to be seen. Soon after, Columbus wrote,
My compass acts strangely. I will not report this to my crew because of their deep superstitions about the area. Days later, Columbus saw a large meteor fall from the sky. He wrote,
A large ball of light has fallen from the sky. It is unsure whether he mentions this occurrence in awe, because of its great size, or in fright. Later on their journey, in that area, Columbus and several of his crew members sighted unexplained dancing lights on the horizon. They wandered around for over a week before finally sighting land.
Glowing Water

Aerial photos taken in 2005 show the phenomenon of glowing water. Whatever causes this phosphorescence to vent up from the Bahama Bank bottoms - if that is its cause - remains a mystery.
The Triangle's location in the Caribbean makes it subject to unpredictable weather patterns. This takes us to Earth changes and the excalation of intense hurricanes in 2005 with more to come in the years ahead.
These weather extremes prey on inexperienced navigators and smaller boats and planes. Water spouts, sudden electrical and thunder storms, and the like, can cause havoc in the area. The Gulf Stream can also be brutal in that region and perhaps has swept away evidence of natural disasters.
Naming the Devil's Sea and the Bermuda Triangle
The first mention of any disappearances in the area was made in 1950 by E.V.W. Jones as a sidebar on the Associated Press wire service regarding recent ship losses in the area. Jones' article notes the mysterious disappearances of ships, planes and small boats in the region, and ascribes it the name "The Devil's Sea."
It was mentioned again in 1952 in a Fate magazine article by George X. Sand, who outlined several strange marine disappearances.
The term "Bermuda Triangle" was popularized by Vincent Gaddis in a 1964 Argosy feature.
The area achieved its fame largely through the efforts of Charles Berlitz in his 1974 book
The Bermuda Triangle. The book consists of a series of recountings of mysterious disappearances of ships and aircraft, in particular, the December 1945 loss of five U.S. Navy Avenger torpedo bombers, known as Flight 19.

The saga of Flight 19 started on December 5th, 1945. Five Avenger torpedo bombers lifted into the air from the Navel Air Station at Fort Lauderdale, Florida, at 2:10 in the afternoon. It was a routine practice mission and the flight was composed of all students except for the Commander, a Lt. Charles Taylor.
The mission called for Taylor and his group of 13 men to fly due east 56 miles to Hens and Chicken Shoals to conduct practice bombing runs. When they had completed that objective, the flight plan called for them to fly an additional 67 miles east, then turn north for 73 miles and finally straight back to base, a distance of 120 miles. This course would take them on a triangular path over the sea.
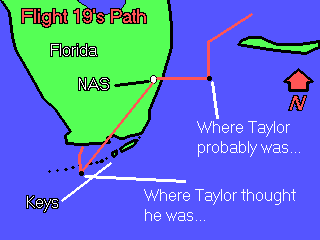
About an hour and a half after the flight had left, a Lt. Robert Cox picked up a radio transmission from Taylor. Taylor indicated that his compasses were not working, but he believed himself to be somewhere over the Florida Keys (the Keys are a long chain of islands south of the Florida mainland). Cox urged him to fly north, toward Miami, if Taylor was sure the flight was over the Keys.
Planes today have a number of ways that they can check their current position including listening to a set of GPS (Global Positioning Satellites) in orbit around the Earth. It is almost impossible for a pilot to get lost if he has the right equipment and uses it properly.
In 1945, though, planes flying over water had to depend on knowing their starting point, how long and fast they had flown, and in what direction. If a pilot made a mistake with any of these figures, he was lost. Over the ocean there were no landmarks to set him right.
Apparently Taylor had become confused at some point in the flight. He was an experienced pilot, but hadn't spent a lot of time flying east toward the Bahamas which was where he was going on that day. For some reason Taylor apparently thought the flight had started out in the wrong direction and had headed south toward the Florida Keys, instead of east. This thought was to color his decisions throughout the rest of the flight with deadly results.
The more Taylor took his flight north to try to get out of the Keys, the further out to sea the Avengers actually traveled. As time went on, snatches of transmissions were picked up on the mainland indicating the other Flight 19 pilots were trying to get Taylor to change course. "If we would just fly west," one student told another, "we would get home." He was right.
By 4:45 P.M. it was obvious to the people on the ground that Taylor was hopelessly lost. He was urged to turn control of the flight over to one of his students, but apparently he didn't. As it grew dark, communications deteriorated. From the few words that did get through it was apparent Taylor was still flying north and east, the wrong directions.
At 5:50 P.M. the ComGulf Sea Frontier Evaluation Center managed get a fix on Flight 19's weakening signals. It was apparently east of New Smyrna Beach, Florida. By then communications were so poor that this information could not be passed to the lost planes.
At 6:20 a Dumbo Flying Boat was dispatched to try and find Flight 19 and guide it back. Within the hour two more planes, Martin Mariners, joined the search. Hope was rapidly fading for Flight 19 by then. The weather was getting rough and the Avengers were very low on fuel.
The two Martin Mariners were supposed to rendezvous at the search zone. The second one, designated Training 49, never showed up.
The last transmission from Flight 19 was heard at 7:04 P.M. Planes searched the area through the night and the next day. There was no sign of the Avengers.
Nor did the authorities really expect to find much. The Avengers, crashing when their fuel was exhausted, would have been sent to the bottom in seconds by the 50 foot waves of the storm. As one of Taylor's colleagues noted,
they didn't call those planes 'Iron Birds' for nothing. They weighed 14,000 pounds empty. So when they ditched, they went down pretty fast. What happened to the missing Martin Mariner? The crew of the SS Gaines Mill observed an explosion over the water shortly after the Mariner had taken off. They headed toward the site and there they saw what looked like oil and airplane debris floating on the surface. None of it was recovered because of the bad weather, but there seems little doubt this was the remains of the Mariner. The plane had a reputation as being a 'flying bomb' which would burst into flame from even a single, small spark. Speculation is that one of 22 men on board, unaware that the unpressurized cabin contained gas fumes, lit a cigarette, causing the explosion.
So how did this tragedy turn into a Bermuda Triangle mystery? The Navy's original investigation concluded the accident had been caused by Taylor's confusion. Taylor's mother refused to accept that and finally got the Navy to change the report to read that the disaster was for "causes or reasons unknown." This may have spared the woman's feelings, but blurred the actual facts.
The saga of Flight 19 is probably the most repeated story about the Bermuda Triangle. The planes, and their pilots, even found their way into the science fiction film classic, 'Close Encounters of the Third Kind.'
Where is Flight 19 now?
In 1991 five Avengers were found in 600 feet of water off the coast of Florida by the salvage ship Deep Sea. Examination of the planes showed that they were not Flight 19, however, so the final resting place of the planes, and their crews is still the Bermuda Triangle's secret.
Kusche's Research
Intrigued by the number of students coming to him looking for information about the Bermuda Triangle, Lawrence Kusche, a reference librarian with Arizona State University at the time of the "Flight 19" incident, began an exhaustive follow-up investigation of the original reports. His findings were eventually published in 1975 as
The Bermuda Triangle Mystery: Solved. Kusche's research revealed a number of inconsistencies between Berlitz's accounts and statements from eyewitnesses, participants, and others involved in the initial incidents. He noted cases where pertinent but late-arriving information went unreported. The Berlitz book included the disappearance of round-the-world yachtsman Donald Crowhurst as a mystery, despite clear evidence that Crowhurst had fabricated the accounts of his voyage, and that his diary strongly suggested he had committed suicide. An ore carrier Berlitz recounts as lost without trace three days out of an Atlantic port was actually lost three days out of a port of the same name in the Pacific Ocean. Kusche argues that a large percentage of the incidents attributed to the Bermuda triangle's mysterious influence actually occurred well outside it.
Kusche came to several conclusions:
With this area being one of the heaviest ship- and airplane-traveled areas in the world, the proportion of losses was no greater than anywhere else.
In an area with frequent tropical storms, the total disappearance of some ships was not unlikely or mysterious, and the number of such disappearances was exaggerated by sloppy research, when a missing boat would be reported in the press, but not its eventual return to port.
In actual disappearances, the circumstances were frequently misreported in the Bermuda Triangle books: the number of ships disappearing in supposedly still, calm weather did not jibe with press weather reports published at the time.
Methane hydrates
An explanation for some of the disappearances focuses on the presence of vast fields of methane hydrates on the continental shelves. A paper was published by the United States Geological Survey about the appearance of hydrates in the Blake Ridge area, offshore southeastern United States, in 1981. Periodic methane eruptions are capable of producing ship-sized bubbles, or regions of water with so much dissolved gas, that the fluid density is no longer capable of providing adequate buoyancy for ships to float. If this were the case, such an area forming around a ship could cause it to sink almost directly and without warning. Experiments have proven that a methane bubble can indeed sink a ship by decreasing the density of the water.
Methane gas can also crash planes. The less dense air causes planes to lose lift. Also, the altimeter of planes (the instrument that measures the altitude) functions on the density of air. Because methane is less dense, the altimeter assumes the plane is climbing. Planes at night or in the clouds, where they can't see the ground, assume that they are climbing and dive, causing them to crash. Also, methane in the engine throws off the mix of fuel and air. Aircraft engines burn hydrocarbons (gasoline or jet fuel) with oxygen provided by the air. When the ambient oxygen levels drop, combustion can stop, and the engine stalls. All of these effects of methane gas have been shown experimentally.
Freak Wave Theory
Research has shown that freak waves up to 30 m (100 feet) tall, capable of sinking the largest ships within moments, can and do happen. Although these are very rare, in some areas ocean currents mean they happen more often than the norm. Such waves have now been hypothesized as a cause for many unexplained shipping losses over the years. The book was a best seller, and many interested readers offered theories to explain the nature of the disappearances. The list includes natural storms, transportation by extraterrestrial technology, high-traffic volumes (and correspondingly high accident rates), a "temporal hole," the lost Atlantis empire from the bottom of the ocean, and other natural and supernatural causes.





